Assignment 4 Report




Assignment 4 Report
Introduction/ Overview
“The new era of VR crane training. with no risk, consequences or experience. Learn with an immersive experience that replicates a real Tower Crane operator in a virtual construction environment.”
Description of the Application
Background: According to statistics from SafeWork Australia, from 2003 to 2015, 47 workers were killed in crane accidents, and on average 240 serious injury claims arise from crane safety incidents every year(1). Based on Lingard’s theory, the key cause of these incidents is due to unsafe practices of tower crane operation, such as inadequate training(2). Thus, sufficient training is critically important in safe crane operation.
Problem: There are two main issues during the training process. The first one is safety problems, new operators do not have enough knowledge to properly operate a crane, which can be dangerous while training. The second issue is the high cost of training. The price to rent a crane is based on the size of that crane, and on average the price is around $200 per hour(3). The purchasing price of a crane is much higher.
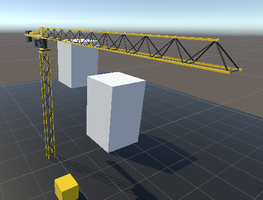
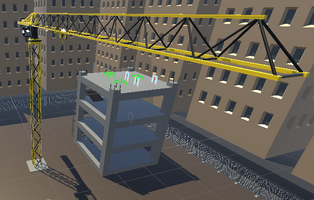
To solve these two problems, our team has designed an application in which the user can operate a realistic virtual crane in a virtual environment. The application consists of a 3D virtual crane that users can sit in, with two joysticks, with one on either side of the user's virtual crane seat. The left joystick can control the rotation of the crane arm by moving the joystick to the left or right, and the trolley travel of the crane by moving the joystick forward or backward. As for the right one, the joystick can control the lowering and raising of the crane’s hook. Near the right joystick, there are two buttons, one green and the other red. The green one can be pressed to connect the hook to objects which are placed on the outside of the crane, and the red one can be pressed to release the object connected to the hook. For the convenience of the user, a camera is placed on the crane's trolley facing directly down, to allow the user to line up the hook of the crane with greater accuracy, this camera outputs in real-time to a screen in the upper right of the crane’s cabin. In addition, to make the whole application more realistic, this application also has some functions like wind simulation options and some safety guideboards.
This application allows users to learn the basic operations of cranes without any physical danger. The only requirement for this application is one VR headset, which reduces the cost of renting or purchasing a real crane.
Description of the interface solution
Unlike training in the real world where just one mistake would harm a property, a business, a reputation, one person or many people, there are no consequences in a virtual world that resembles much of the real world.
We choose Virtual reality because it resembles a real experience, virtual reality is such a powerful teaching simulation tool. According to [Zielinski D] trainees who receive VR training have a great impact on their field of training. The crane simulator enables the trainees or prospective employees to get fully immersed in any scenario that they might encounter. We believe a precise simulation of the scenarios that staff members in tower crane work encounter is produced using virtual reality experiences.
Why we choose to apply VR to this application because when it comes to simulations, virtual reality (VR) makes an immersive virtual surrounding, unlike AR which creates contact with an object in a real-world scene. AR minimizes crane operations whereas the users still interact with virtual objects in the real world. While applying VR technology the user is completely cut off from the real world and submerges themself in a virtual setting where the user could interact with multiple operations to resemble a real-life crane experience.
One key component of operating a crane in virtual reality is depth perception. The head-mounted displays have an impact on how much depth is perceived inside the crane cabin. Depth perception is important because the user gets to experience a tower crane that is placed high above the construction site, where the operators are tasked with lifting objects to assist in the construction of the building with various lifting objectives that require different techniques, and simultaneously having an accurate control can train users on how to operate the crane properly and avoid risks.
Significance of the interface technology (VR or AR) in the context of the application
One of the main VR training key features would be increased efficiency. With the use of the VR crane simulator, future crane operators can receive training more quickly, easily, and affordably. With the use of this application, trainees can practice handling uncommon and unusual situations that may arise while performing their normal jobs, such as breaking ropes.
In a crane simulation using motion control, VR Joysticks are much more similar and practical than using A mouse, keyboard or controller. When it comes to training, the user would learn more practical knowledge than just theoretical while having a two motion controllers that should operate the way the two crane should.
Real Tower Crane stick controls
As shown in the Figure above, VR motion controllers have a much similar resemblance to real tower crane cabin controls. The two VR controllers have a better relationship between the user and the two virtual control objects.
Interaction Design
The crane has a camera on the trolley pointing down, and this camera is viewable on a screen in the cabin. This is to help the user line up the hook which is lowered from the trolley and is also required for the user to pick up objects behind other objects that would block the direct line of sight of the user to that object.
The crane has a joystick on either side of the user's position, these joysticks are grabbable by the user, and these can be moved around when grabbed. These joysticks are required because they are used to control the rotation of the crane and the travel of the crane trolley backwards and forwards, as well as the lowering and raising of the crane's hook, and these make up the basic controls of a tower crane. Without these joysticks, the crane would not function like a real crane, which would make the training of real crane operation ineffective. The joysticks provide feedback to the user via the hand controller's vibration, to let the user know they are moving something even when not looking directly at the moving part. The joysticks can be used in VR the same way as in a real crane and have an identical control scheme, giving the joysticks a high level of affordance.
The crane has 2 buttons on the right side of the cabin that can be pressed by the user's index finger, and these buttons hook or unhook objects to the crane's hook. These interactions are required because in real life a crane has people on the ground to hook and unhook loads, but the user needs the ability to do this themselves, as they are alone in the VR application. When an object is hooked using the green button it will move to a pressed position to indicate that an object is hooked, following Don Norman's design principle of feedback.
The hook can connect to hookable objects when it is close enough and the user presses the green hook button, and attaching them to the hook allows them to be moved with the crane. This is required to allow the user to move these hookable objects using the crane's controls, without this interaction the crane would not be functional as objects would not be moveable.
We have abstracted away the additional workers that would be on the ground to hook the cranes hook onto an object, and this was done as there would not be any other people in the application, and so the hooking needs to be atomized.
An image of a man doing crane hand signals will appear near where the user needs to either pick up or drop off hookable objects, and the image will change depending on which way the user needs to move the crane to position the object in the right area, and shows a hand signal to stop for when the user has positioned the object correctly and can unhook. This is required for the user as learning these hand signals is an important part of learning to operate a crane.
In the final version of this application, we would also like to have a screen that displays the position of each of the crane's moving parts, like the distance that the hook is from the crane arm, it would also display wind conditions and the weight of the load. This would be to more completely simulate a real crane, which has this information displayed, and the more accurately we can simulate the real operation of the crane, the greater the efficiency of the training. We would also like to have collision detection on the load, which would let the user know when they have done something wrong and hit something with the crane.
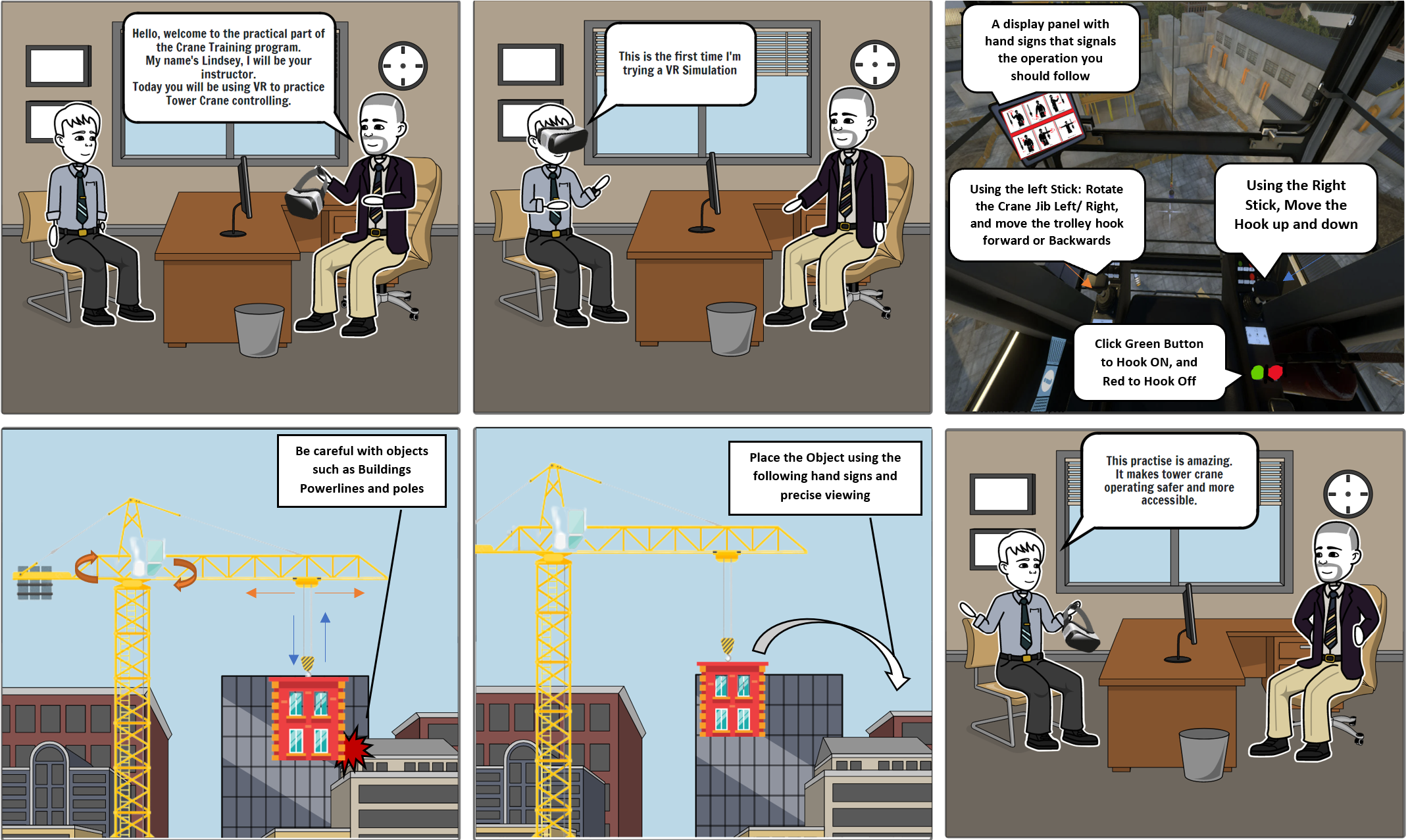
To use this application you would go to a crane training company with qualified crane tutors, to ensure that the training being done is adequate, and to answer any questions that the user might have. When you use this application you will be sitting down to mirror how you would be sitting inside a real crane.
This application would be used with a tutor that would be able to check that the user is operating the crane correctly, and can also control the scenario that the user is in, such as adding wind or other environmental factors, so that the user can learn to operate the crane in these situations.
Initial Technical Development
A prototype has been created in which the user can use 2 joysticks to control the crane, with the left joystick for rotating the crane and moving the trolley, and the right joystick for lowering and raising the crane hook, along with 2 buttons for hooking and unhooking the load onto the cranes hook.
The prototype consists of some objects that the user can move with the crane at a basic plane level, to test the use of the crane's controls.
Also included in the prototype is a gif of various hand signals being used that the user has to observe and correctly follow. The completed application would likely have a 3D model doing the hand signals, to make it easier for the user to see.
A system for a crane operator tutor to activate various dangerous scenarios will also be added, which would allow the tutor to start scenarios such as wind, which the user would then have to react to.
We will also be changing or adding features based on the feedback we receive from the testing session.
The application we are creating will be usable with Oculus VR headsets
Initial 3D Models
Crane
The crane is what the user controls, sitting within the cranes cabin. It is made up of the cranes tower, crane arm, trolley, cabin and hook. Made by Frederick.

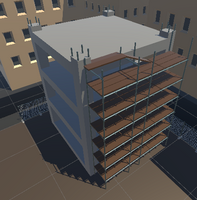
Construction Site
The construction site is a place where the user can drop items onto with the crane. Made by Frederick.
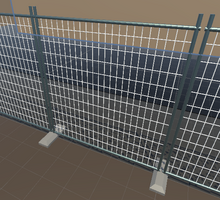
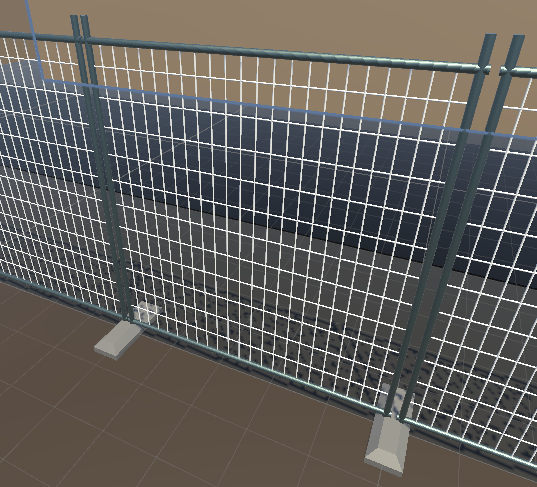
Fences
The fences surround the construction zone and make up part of the virtual environment. Made by Frederick.
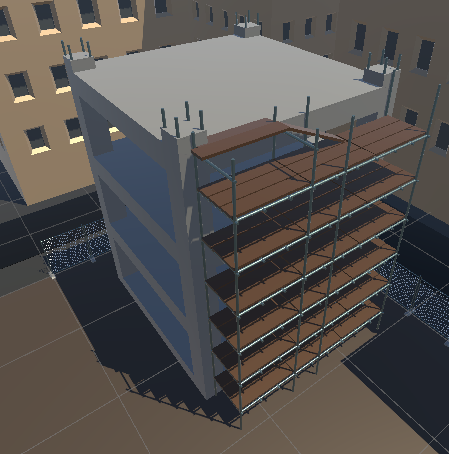
Buildings
The buildings surround the outside of the construction zone and make up part of the virtual environment and block the users view of the infinite skybox void. Made by Frederick.

Pipes
The pipes are one of the objects the user can pick up with the crane. Made by Frederick.

Girder
The girder is one of the objects the user can pick up with the crane. Made by Frederick.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the application contains several components and functions, which satisfy the basic requirements of crane operator training. In the meanwhile, the application uses VR technology to make the training process safe and reduce the cost of the training.
References
- Research Summary, 2020, Crane Safety in Construction <https://www.centreforwhs.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0009/875394/Crane-safety-in-construction-Summary.pdf>
- Lingard, H, Cooke, T, Zelic, G & Harley, J 2021, 'A qualitative analysis of crane safety incident causation in the Australian construction industry', Safety science, vol. 133, p. 105028.
- Crane division, n.d., James Contact Supplies, <https://irp-cdn.multiscreensite.com/27e771a2/files/uploaded/F1010%20Crane%20Schedule%20of%20Hire%20Rates..pdf>
- Zielinski D, The Growing Impact of Virtual Reality Training, SHRM
Storyboard Creator: <https://www.storyboardthat.com/>
Used to create the Storyboard.
Storyboard crane cabin Image: <https://www.iti.com/vr/tower-crane-training-simulator>
By: ITI VR
Used to display the crane cabin in the storyboard.
Get KIT 208-724 Assignment 4-5
KIT 208-724 Assignment 4-5
| Status | Released |
| Authors | xepries, Nirash Jude, shengbow |
| Genre | Simulation |
| Tags | crane, tower-crane |
More posts
- Assignment 5 ReportOct 27, 2022

Leave a comment
Log in with itch.io to leave a comment.